
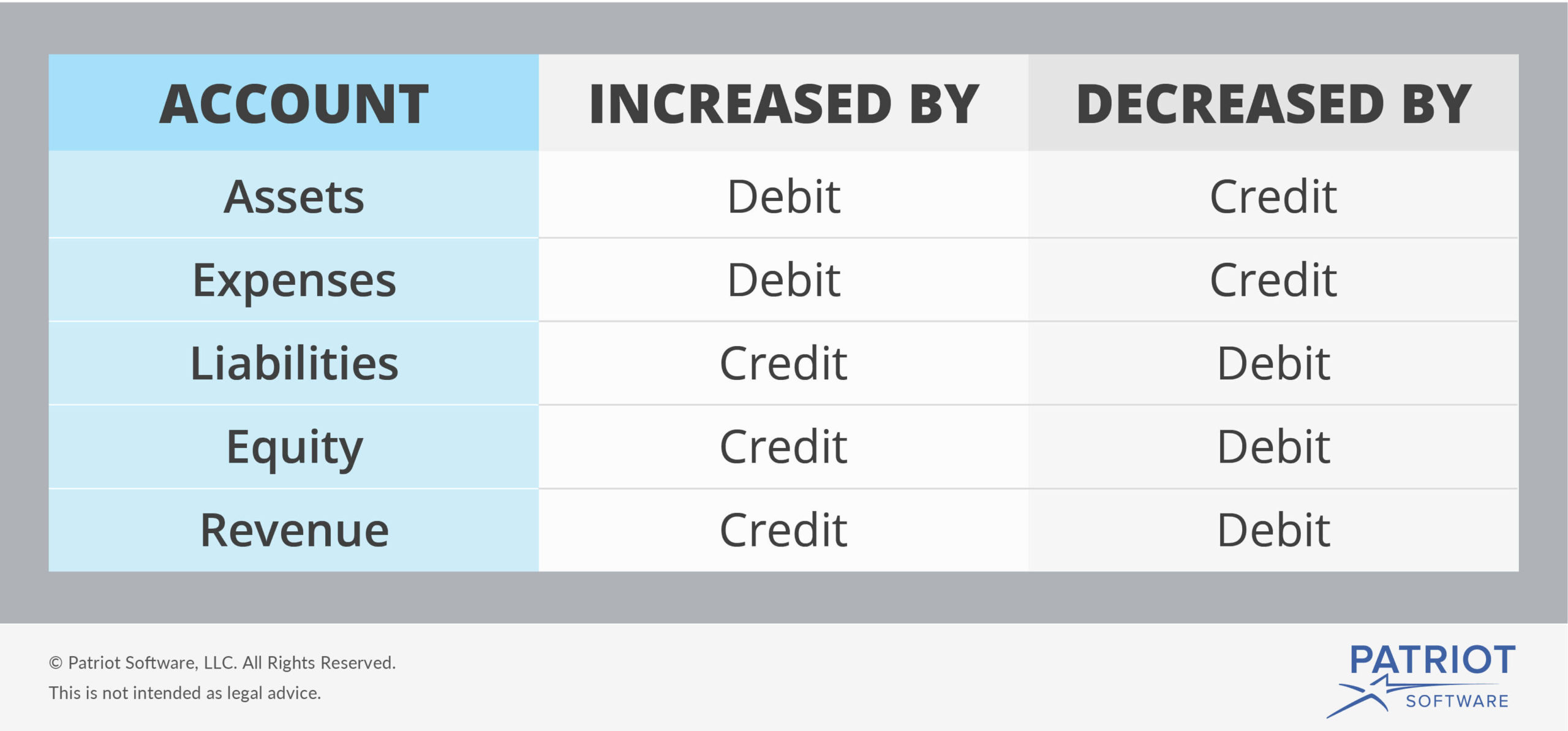
Spending cash, selling inventory, or customers paying down their debts are all examples of credits since these resources are leaving your company. As you process more accounting transactions, you’ll become more familiar with this process. Take a look at this comprehensive chart of accounts that explains how other transactions affect debits and credits. As long as the total dollar amount of debits and credits are equal, the balance sheet formula stays in balance. This entry increases inventory (an asset account), and increases accounts payable (a liability account). A company’s general ledger is a record of every transaction posted to the accounting records throughout its lifetime, including all journal entries.
Thus, the accounts payable turnover ratio demonstrates your business’s efficiency in meeting its short-term debt obligations. Accounts payable is a general ledger account that showcases the amount of money that you owe to your creditors/suppliers. If yo receive an invoice mentioning the payment terms from your supplier, it then gets recorded in your accounts payable ledger.
Accounts receivable are goods supplied to a customer on credit, owed at a later date. Accounts payable typically cover a range of short-term debts harvest accounting from purchases of goods and services. The vendor would send you an invoice for the inventory of $300, this invoice would be a bill payable.
However, in some cases, it can also be debit when there is a decrease at the time the company settles those accounts payable or at the time the company discharged the liabilities. Cases in which companies can classify their accounts payable balances as non-current are rare. Bank debits and credits aren’t something you need to understand to handle your business bookkeeping. All changes to the business’s assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses are recorded in the general ledger as journal entries. Cash is increased with a debit, and the credit decreases accounts receivable. The balance sheet formula remains in balance because assets are increased and decreased by the same dollar amount.
At the end of each year, they present their accounts payable balances on their balance sheet. For bookkeeping purposes, each and every financial transaction affecting a business is recorded in accounts. The 5 main types of accounts are assets, expenses, revenue (income), liabilities, and equity.
Like Accounts Payable, AR could refer to the department responsible for this money. Automation ensures that data is accurately captured and processed, minimizing mistakes that can occur with manual handling. This leads to more reliable financial records and fewer discrepancies to resolve.
But choosing not to ignores a significant opportunity for growth, especially if you can run AP reports with just the click of a button. Reports help you maintain healthy AP processes, ensure accurate financial statements, build better supplier relationships, and improve financial decision-making. The ticket is entered as a credit in the AP ledger because the ticket amount will be paid to an external ticketing agent and as a debit under the travel expenses ledger. As explained earlier, not all the money owed by a company to creditors is eligible for AP entry. When you make a payment on a loan or settle a bill, you debit the account, which reduces what you owe.
The transactions relating to accounts payable are repetitive in nature. Therefore, many companies use a special journal known as purchases journal for recording these transactions. However, small companies with low transaction volume don’t maintain special journals.
The offsetting credit entry for such a transaction is made to the cash account, because the cash worth $200,000 gets reduced. The debit offset for this entry generally goes to an expense account for the good or service that was purchased on credit. The debit could also be to an asset account if the item purchased was a capitalizable asset. When the bill is paid, the accountant debits accounts payable to decrease the liability balance. The offsetting credit is made to the cash account, which also decreases the cash balance. When a purchase is made on credit, the transaction is debited from the relevant expense account but cannot be credited to the vendor, as the bill is paid later.
You must process your invoices on a regular basis, regadless of the number of vendors you have, so you can follow the above procedure either weekly or fortnightly. This can help to reduce your workload at the months-end, and following a weekly or a fortnightly accounts payable cycle can help you avoid late payments. However, before streamlining your accounts payable process, it is essential to understand what the accounts payable cycle is. The accounts payable cycle is a part of your purchasing cycle, and includes activities essential to completing a purchase with your vendor. Accounts payable, if managed effectively, indicates the operational effectiveness of your business.